This article has been amended to reflect an update on the FDA decision in July 2024.
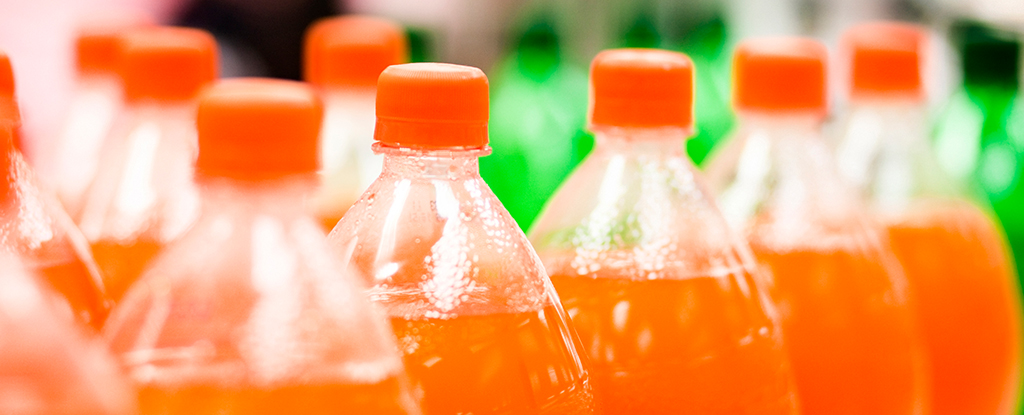
An ingredient once commonly used in citrus-flavored sodas to keep the tangy taste mixed thoroughly through the beverage has finally been banned for good across the US.
The FDA has now revoked the registration of a modified vegetable oil known as BVO in the wake of recent toxicology studies that make it difficult to support its ongoing use.
“The proposed action is an example of how the agency monitors emerging evidence and, as needed, conducts scientific research to investigate safety related questions, and takes regulatory action when the science does not support the continued safe use of additives in foods,” James Jones, FDA deputy commissioner for human foods, explained when announcing the proposal.
BVO, or brominated vegetable oil, has been used as an emulsifying agent since the 1930s to ensure citrus flavoring agents don’t float to the top of sodas. Sticking a dozen bromine atoms to a triglyceride creates a dense oil that floats evenly throughout water when mixed with less dense fats.
Yet that’s not BVO’s only trick. Animal studies have strongly implied the compound can slowly build up in our fat tissues. With bromine’s potential ability to prevent iodine from doing its all-important work inside the thyroid, health authorities around the world have been suspicious of the emulsifier’s risks for decades.
In fact, BVO is already banned in many countries, including India, Japan, and nations of the European Union, and was outlawed in the state of California in October 2022 with legislation due to take effect in 2027.
Yet the FDA has been slow to convince. In the 1950s, the agency regarded the ingredient as generally recognized as safe (GRAS); an official classification afforded items that have either been appropriately tested or – for ingredients in common use prior to 1958 – don’t appear to be harmful.
That changed the following decade when questions were raised over its possible toxicity, prompting the FDA to overturn its GRAS classification for BVO and temporarily limit its use to relatively small concentrations of no more than 15 parts per million exclusively in citrus-flavored drinks.
Data on the risks posed by even these small amounts of BVO over time hasn’t been easy to collect, relying heavily on long-term studies that re-evaluate health effects in a significantly-sized sample of people. Yet the evidence has been slowly mounting.
A UK study in the 1970s found bromine was building up in human tissues, with animal studies linking high concentrations of BVO with heart and behavioral problems.
It’s taken time, and a number of further studies, but on the back of more recent animal studies based on relative concentrations of BVO humans are likely to ingest, the FDA is finally convinced there is sufficient evidence to ban its use altogether.
Most major soda drink companies are fortunately ahead of the game. PepsiCo and Coca-Cola Co. have been phasing the ingredient out of their products over the past decade.
“Over the years many beverage makers reformulated their products to replace BVO with an alternative ingredient, and today, few beverages in the US contain BVO,” said Jones.
The ban could be a sign of more things to come, with Jones announcing the agency is reviewing regulations that authorize the use of certain food additives, with a view to automatically prohibit the approval of any food coloring agents found to cause cancer in humans or animals, making for a more nimble bureaucratic process.
The final call on the FDA’s reclassification of BVO went through a lengthy review process that has now been completed.
With suitable alternatives to BVO already being used to make citrus drinks around the world taste tangy down to the very last drop, the ingredient isn’t likely to be missed.
An earlier version of this article was published in November 2023.