Disposable plastic containers could be leaching dangerous chemicals into your takeaway food, potentially increasing your risk of cardiovascular disease.
In experiments on rats, researchers in China have found evidence that drinking water exposed to the various chemical additives that seep from heated plastic packaging causes changes to the body, that begin with altered gut bacteria.
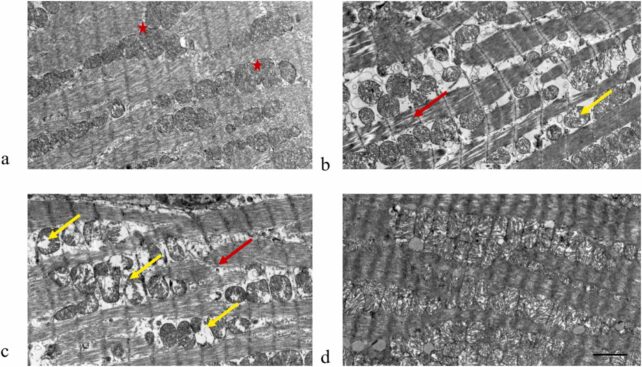
Rodents that ingested this cocktail of plastic contaminants for just three months showed broken or misaligned fibers, inflammatory cell infiltration, and mitochondrial swelling in their heart tissue. They also showed bleeding between myocardial cells, as marked by the black pentagrams in the image below:
Whether or not the same occurs in the human body is unknown, but the findings suggest that heated plastic containers may not be a safe vehicle for food.
As we wait for more research, the authors of the study at Ningxia Medical University in China argue, “It is essential to avoid using plastic containers for high-temperature food”.
Their experiments on rats were prompted by a survey of 3,179 older adults in China. Those who reported higher exposure to plastic on a questionnaire were more likely to suffer congestive heart failure.
Other recent and concerning research has found microplastics accumulating in blood clots within the human brain, heart, and legs, so epidemiologist Yueping Wu and their colleagues decided to investigate the cardiovascular effects further.
Over the course of three months, they fed 24 rodents the chemicals that are leached from plastic containers when they are heated by boiling tap water, which include compounds such as BPA, phthalates, and various plasticizers. These ‘leachates’ were produced by placing plastic containers in hot tap water for durations of 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
Ultimately, rodents that drank the contaminated water had an altered intestinal microenvironment compared to the eight control rodents that did not. Their gut microbiomes had altered significantly after exposure to plastic and its chemicals, including changes to flora associated with inflammation.
The blood of these exposed animals also showed a spike in inflammatory immune messengers, which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
“These changes might be linked to plastic product leachates disrupting microbiota and inflammatory factors, which then trigger inflammation and myocardial damage,” the authors explain.
Heat causes plastic to break down more easily, but even bottled water, which is usually kept at room temperature or colder, seems to be swimming with microplastics.
Recently, studies have shown that microwaving plastic food containers can release microplastics and nanoplastics into the meal, even if the containers claim to be microwave-safe. As few as three minutes can release billions of tiny plastic particles.
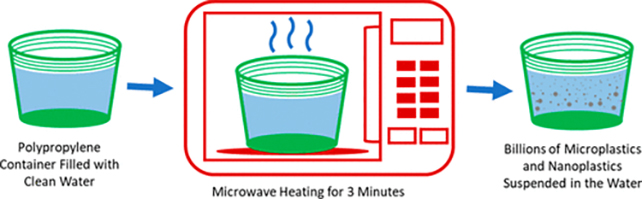
How many of those plastic particles are absorbed into the body when ingested is unknown. It’s also a mystery as to how long the fragments stick around for.
Some studies on clogged arteries in human patients have found tiny fragments of plastic accumulating in more than 50 percent of plaques. Within roughly 34 months of surgery, those with plastics in their arteries were 4.5 times more likely to have a heart attack, stroke, or death compared to those where no plastic was detected.
When the body is exposed to plastic contaminants, researchers suspect there’s a chance the additives can reduce the activity of antioxidant enzymes and trigger the body’s inflammatory reaction, leaving it exposed to cardiovascular damage.
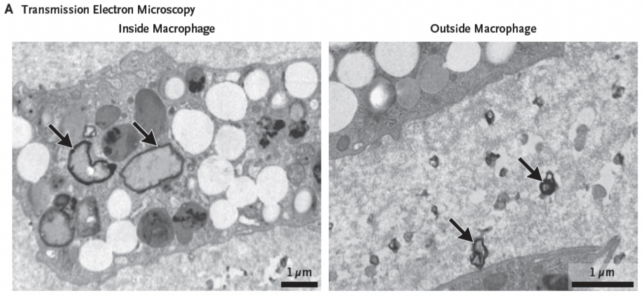
The potential health effects of plastic pollution are only just beginning to emerge, but the mounting evidence is not exactly inspiring hope.
In a study published last year, scientists discovered that when people put hot, disposable plastic cutlery in their mouths, it reduces their diversity of intestinal microbiota.
The next time you order takeaway, you might want to think about the heat of the food and the material of the packaging it might come in.
The study was published in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.





