The rapid advancement of chipmaking technology over the past two decades has been primarily driven by the continuous scaling of silicon technology, commonly known as Moore’s Law. However, as we approach the physical limitations of silicon, the industry is shifting its focus towards nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes, graphene, and TMDs, which promise unprecedented chip functionality.
Nanomaterials hold the potential to revolutionize various electronic devices, including high-performance transistors, low-power sensors, and quantum devices. The global nanotechnology market is projected to grow from $79.14 billion in 2023 to $248.56 billion by 2030, according to Fortune Business Insights Research, showing just how bright its future is expected to be.
The lack of control in existing nanotechnology production methods, primarily chemistry-based, has hindered their commercialization to date. This is where Swiss nanotechnology firm Chiral, which recently announced a $3.8 million funding round, comes in.
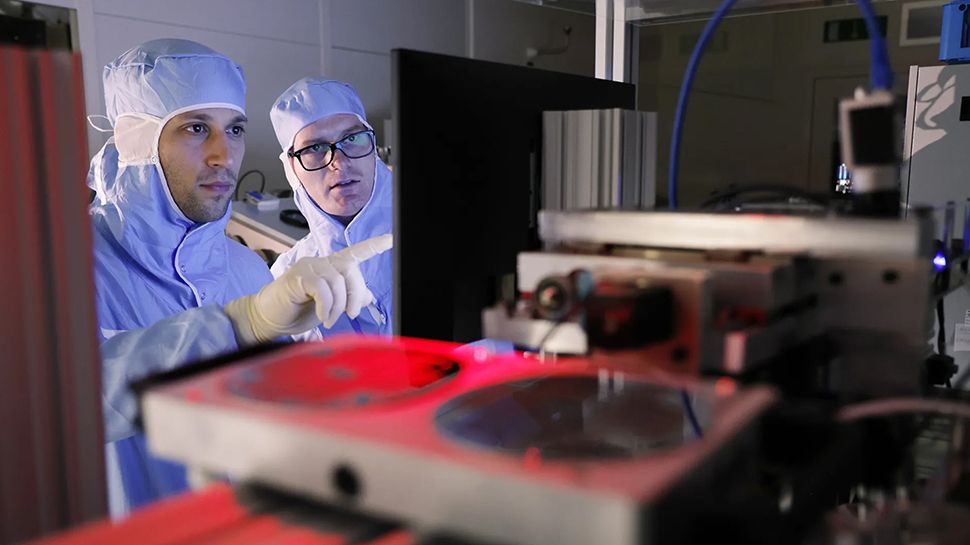
Automated robotic machines
Chiral’s journey began as a national research project at the Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology, where co-founders Seoho Jung, Natanael Lanz, and Andre Butzerin were PhD students. After four years of R&D and the successful creation of a prototype machine that was 100 times faster than existing systems, the team incorporated Chiral in June 2023.
The firm plans to use high-speed, automated robotic machines to integrate nanomaterials into devices. These machines can reportedly place materials as small as micrometers or even nanometers on chips with unprecedented precision and control, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods.
Chiral’s pre-seed funding round was co-led by Founderful and HCVC, and Pascal Mathis, Founding Partner at Founderful, said: “Chiral’s AI- and robotics-based technology lets us envision a future where nanomaterial-based chips are being produced at the scale needed for commercialization – a major bottleneck up until now.”