I didn’t expect Google Glass to make a minor comeback at Google I/O 2024, but it did, thanks to Project Astra.
That’s Google‘s name for a new prototype of AI agents, underpinned by the Gemini multimodal AI, that can make sense of video and speech inputs, and smartly react to what a person is effectively looking at and answer queries about it.
Described as a “universal AI” that can be “truly helpful in everyday life”, Project Astra is designed to be proactive, teachable, and able to understand natural language. And in a video ,Google demonstrated this with a person using what looked like a Pixel 8 Pro with the Astra AI running on it.
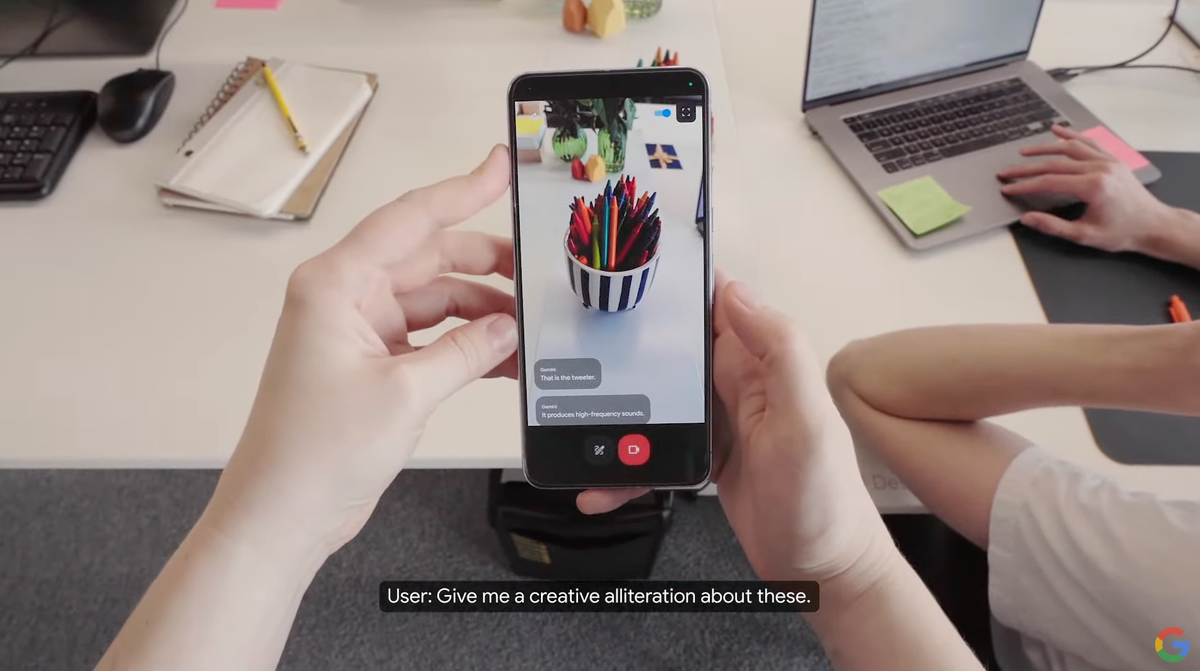
By pointing the phone’s camera at room, the person was able to ask Astra to “tell me when you see something that makes sound”, to which the AI will flagged a speaker it can see within the camera’s viewfinder. From there the person was able to ask what a certain part of the speaker was, with the AI replying that the part in question is a tweeter and handles high frequencies.
But Astra does a lot more: it can identify code on a monitor and explain what it does, and it can work out where someone is in a city and provide a description of that area. Heck, when promoted, it can even make an alliterative sentence around a set of crayons in a fashion that’s a tad Dr Zeus-like.
It can can even recall where the user has left a pair of glasses, as the AI remembers where it saw them last. It was able to do the latter as AI is designed to encode video frames of what it’s seen, combine that video with speech inputs and put it all together in a timeline of events, caching that information so it can recall it later at speed.
Then flipping over to a person wearing the Google Glass ‘smart glasses’, Astra could see that the person was looking at a diagram of a system on a whiteboard, and figure out where optimizations could be made when asked about them.
Such capabilities suddenly make Glass seem genuinely useful, rather than the slightly creepy and arguably dud device it was a handful of years ago; maybe we’ll see Google return to the smart glasses arena after this.
Project Astra can do all of this thanks to using multimodal AI, which in simple terms is a mix of neural network models that can process data and inputs from multiple sources; think mixing information from cameras and microphones with knowledge the AI has already been trained on.
Google didn’t say when Project Astra will make it into products, or even into the hands of developers, but Google’s DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis said that “some of these capabilities are coming to Google products, like the Gemini app, later this year.” I’d be very surprised if that doesn’t mean the Google Pixel 9, which we’re expecting to arrive later this year.
Now it’s worth bearing in mind that Project Astra was shown off in a very slick video, and the reality of such onboard AI agents is they can suffer from latency. But it’s a promising look at how Google will likely integrate actually useful AI tools into its future products.